Albacore Tuna

North Pacific albacore tuna, a highly migratory species, is a fast-swimming schooling fish that migrates annually across the Pacific Ocean. Large schools of albacore can be 19 miles wide and move at speeds up to 50 miles per hour. The fish have to swim continuously to keep oxygenated water moving over their gills. Fully grown, albacore tuna can weigh up to 80 pounds, but most caught off the West Coast are 10-20 pounds and 3-5 years old. Albacore caught by West Coast trollers are a relatively young age, and thus have accumulated lower levels of mercury than albacore caught by other methods. Albacore can be caught far off shore, with some boats going out more than 200 miles. With very few natural predators, albacore are top carnivores within the marine food web and consume a wide variety of prey including sardines, anchovy, and squid.
Overall availability
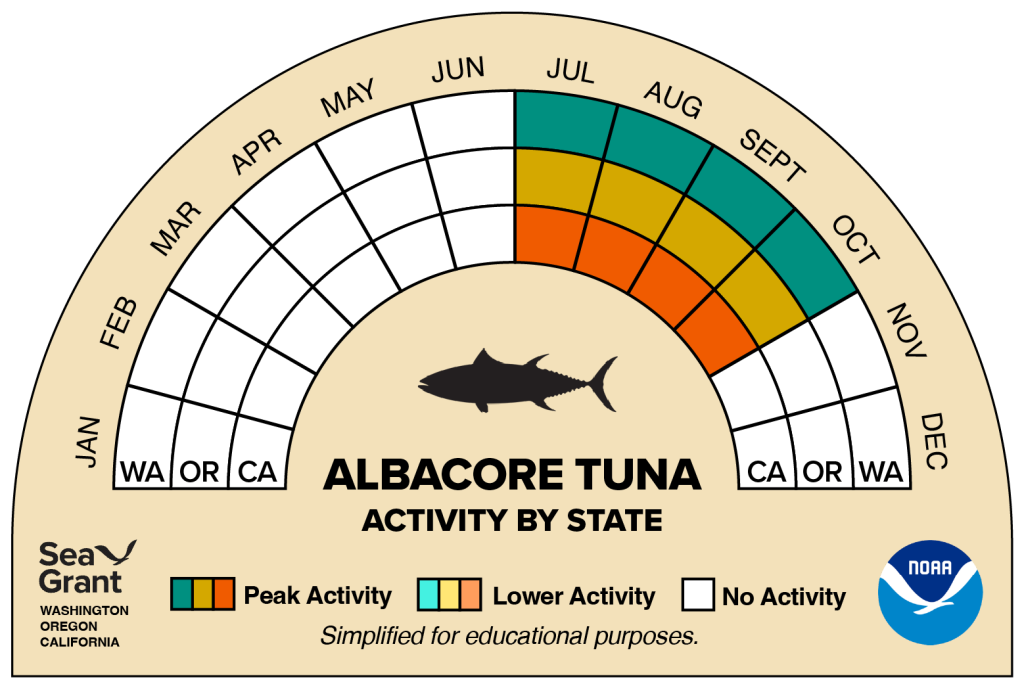
Albacore tuna is fished off all three West Coast states, California, Oregon and Washington. While it may be fished year-round in some regions, the fish follow a warm water current that arrives off of the West Coast in the summer. As a result, the commercial albacore fishing season typically spans mid-summer to early fall, depending on the water temperature. Albacore may be sold as fresh and frozen whole and portioned loins and steaks, and as prepared products such as smoked, canned, and seasoned in vacuum-sealed pouches. It is often sold dockside during summer months in Oregon and Washington and less consistently in Northern California.
Management
Albacore is caught by troll gear in all three states and pole in California. The fishery is managed internationally through the Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission and the Western Central Pacific Fisheries Commission, as well as regionally by the Pacific Fishery Management Council’s Highly Migratory Species Plan in cooperation with state Departments of Fish and Wildlife (CA, OR, WA).
More Information
Other Common Names: Longfin tuna, Tombo tuna








